
These are available for jessie, stretch, buster and sid, and are further discussed in a blog post.In this article, I will take you through the steps to Install and use Docker on Debian 11. John Goerzen has a set of Debian images which feature a full standard init system, cron, SMTP server, etc. You may also be interested in the Debian adaptation of baseimage-docker made by obergix, which also uses runit to control services run inside a container. See for a description of how to automate image creation for services running Debian, which describes a way to ensure services will be started properly by runit inside the containers. Running services inside Docker containers Of course, you'll then need to name that image in your preferred way, to reuse it in later Dockerfiles, for instance with : FROM YOURUSER/minbase:sid See Cloud/CreateDockerImage for a detailed procedure (similar to the one used for the ready-made images), using the classical debootstrap Debian tool.
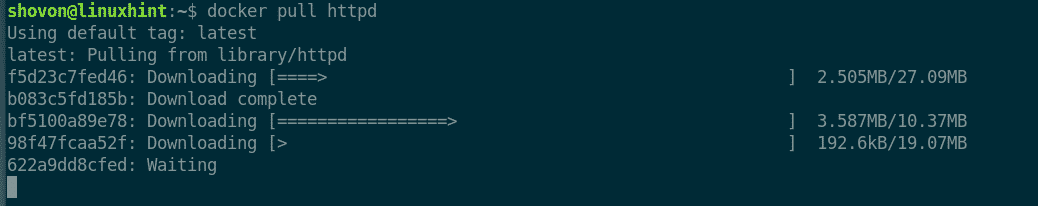
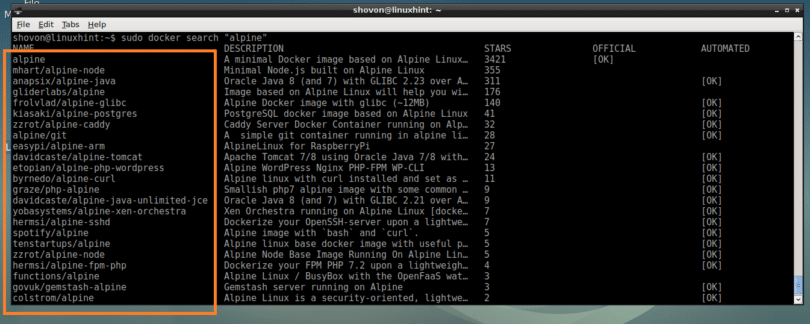
However you may not trust their maintainer on having done the right thing for you. The way these images are generated is now documented quite well in the image description (see below for pointers on re-creating images).Īll that it takes to construct a container based on this image, is to use a declaration like the following in a Dockerfile : FROM debian:sid Ready-made images from docker.io's official Debian repositoryĭebian images provided in docker.io's official repositories (their "official images") are listed on their official debian images repository. In Docker terminology, an image is an object that you can download, and reuse to instantiate new containers. Docker upstream also provides packages (for multiple different debian version): ĭebian images are available in the docker.io official repository, but you may as well create some yourself (see more details on both options below). Thus, the safer choice is to never add a user account - even your own - to the docker group, so that Docker commands can only be used via sudo.ĭocker is a solution for the management of lightweight process containers.ĭocker can be installed from buster (or newer) repositories (see the docker.io package). Access to Docker commands effectively grants full root power.Īlso, Docker doesn't have any equivalent to sudo's password check, which means that a successful arbitrary-code-execution exploit against a user who is in the docker group effectively grants the attacker root.
This makes it trivial for a malicious user to read and alter sensitive system files, or for a careless user to allow a malicious containerized app to do so. The Docker daemon has setUID root, and by design allows easy access as root to the host filesystem.

Docker group membership is more dangerous than sudo


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
